Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
ACL rules can be applied to various to various components such as records, tables, and fields.
Record ACL
Rulesrules
Record ACL rules include table and field names.
- The A table name specifies the table to secure. If a table has extending tables, then this table is called a parent table. The ACL rules for a parent table work for its child tables as well.
- The A field name specifies the field to secure. As a result of table extension, some tables share the same fields. The ACL rule for a field in a parent table works for the for the same field in child tables as well.
ACL rules can restrict access to the operations listed in the following table below. See the the ACL article to learn more.
The processing of record ACL rules processes checking are processed in the following order:
- Table ACL rules.
- Field ACL rules.
This order establishes a hierarchy: first, the users gain access to a more general object and then to a more specific one. To access a record, the users must pass match to both table and field ACL rules.
- If a user has no access right to the table by the ACL rule does not permit access, then the access to all fields in the table is denied, even if the user meets the field ACL rule requirementsconditions.
- If a user has an access right to the table by the ACL rule allows access, but a has no access right to table fields based on the field ACL rule denies it, then the access to the restricted fields is denied.
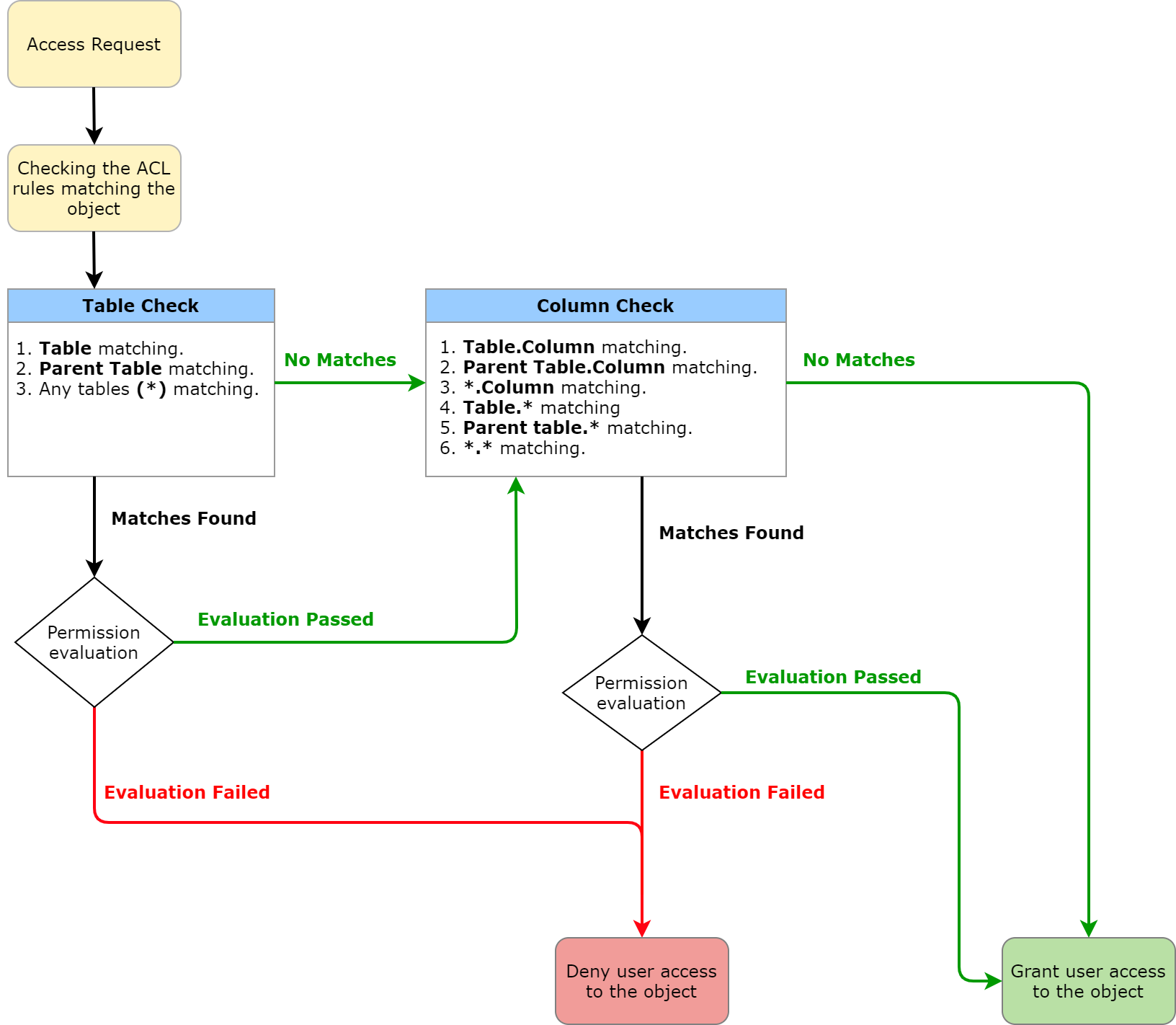 Image Removed
Image Removed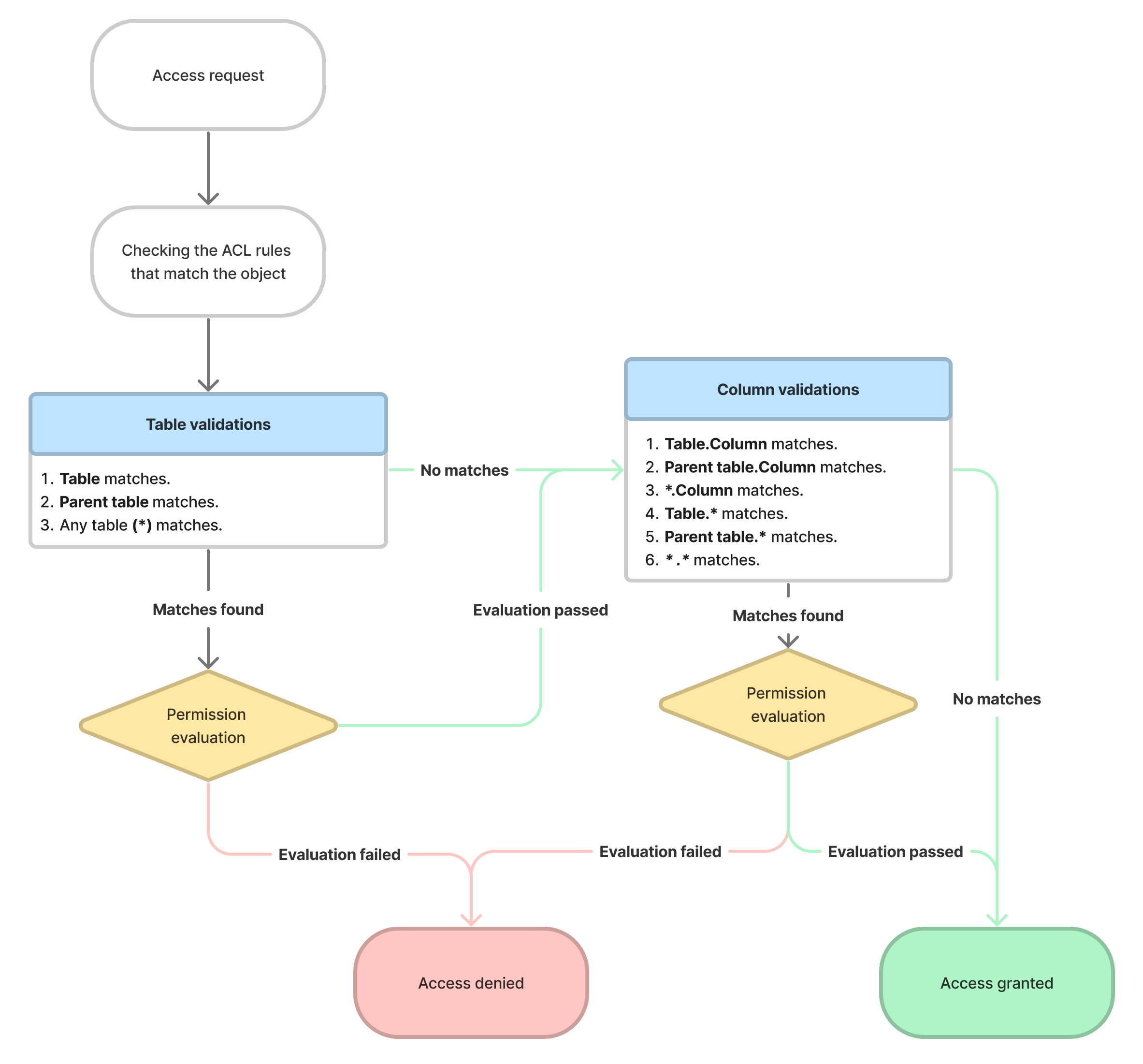 Image Added
Image Added
Table ACL
Rulesrules
First, a user should match the conditions of the table ACL rule must be passed. The base system includes wildcard (*) ACL rules that match any table or any column. So the user must should always pass match at least one table ACL rule. Access The access to some the specific tables is secured by additional table ACL rules.
Table ACL rules processes checking are processed in the following order:
- Table. For example, Incident.
- Parent table. In our the given example, it will be is the Task table.
- Match any table name (*).
If a user does not meet any table ACL checksrules, the access is restricted to all the fields in any tables. If a the user meets a the table ACL checkrule, they are to pass meet the field ACL rules.
Field ACL
Rulesrules
When a user matches the table ACL rule is passed, the field ACL rules start checking are processed in the following order:
- Table and column name. For example, incident.number.
- Parent table and column name. For example, task.number, parent table of the Incident table.
- Any table (*) and column name. For example, *.number.
- Table and any fields field (*). For example, incident.*.
- Parent table and any columnsfield. For example, task.*.
- Any table (*) and any fields field (*). For example, *.*.
The user must pass users should match the field ACL rule; otherwise, the access to the table fields will be is denied. For example, a user wants to access the Number field in the Incident table. In this case, the user must first pass the table ACL rule.
If the user matches the first field ACL rule is passed, the ACL evaluation check stops at the column level: the system stops searching other matching field ACL rules. For example, if a user meets the requirements conditions of the field ACL rule for for incident.number, the system stops searching for other ACL rules that secure the Number field in the Incident table, i.e., so only step 1 is takenperformed.
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|