Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
Inbound email actions are most commonly used to process emails. For example, if an incoming email contains “Incident” in the subject line, the system creates an incident record.
Inbound email actions are similar to business rules in the usage of scripts and conditions that perform actions on the target table. Inbound email actions verify emails for defined conditions and marks features that associate an email with a task. If the conditions are met, the inbound email action performs the pre-configured activities. There are two types of them:
- Record Actionaction: runs a specified script.
- Reply Email: when triggered, sends email: sends a reply email.
Unlike Notification Rules, inbound email actions enable the user to interact with the records in the system.
For example, while processing an incident in the Information Neededneeded state, the system inserts the body of this email to the Additional Commentcomment field in the Activity Feed when the caller sends their response. To do so, an inbound email action is created. The condition for this action is that the caller's email contains a specific the presence of a certain text in its the subject , and the same task number it includes matches the one as in the incident record. That is, the inbound email action defines what happens in the system after receiving an email.
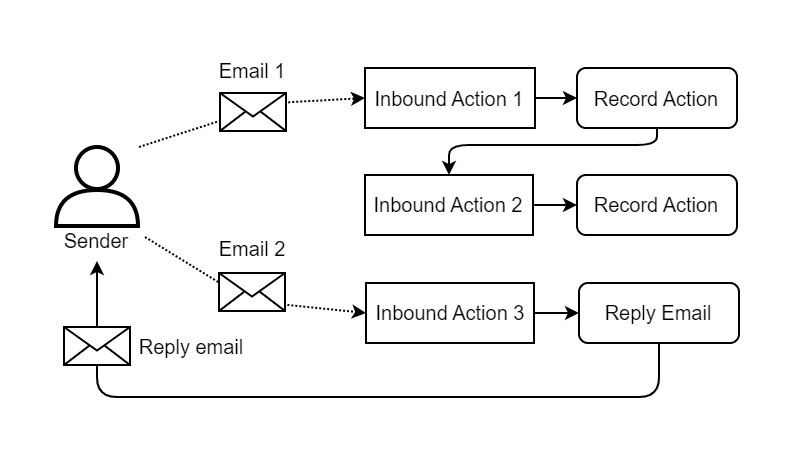 Image Removed
Image Removed Image Added
Image Added
| Note |
|---|
To process inbound email, set up the default email account. See the Email Accounts article to learn how to configure the default email accountdo it. |
Inbound action chain
Inbound actions include three major groups of parameters:
An action to execute when an email is received. It is defined with a script.Email processing chain
The order in which an incoming email is processed is determined by the following parameters:
- A condition that an email should meet for the action to be executed.
- An action type to execute when an email is received.
- Parameters that control the processing flow.
The third group of parameters is required to organize multiple inbound email actions in a way that they check an incoming email to match the condition defined in each of them, in a certain order. The less is the value in the Order field of an inbound action, the earlier this inbound action checks if a received email matches its execution condition. As a result, each email goes through an ordered chain of condition checks, from the inbound action with the least Order value to the one with the biggest, with the following processing logic: One incoming email can trigger execution of none, one or several actions in a row, depending on the values of the Active, Order, and Stop processing when complete fields of the action.
The inbound email actions are processed starting from the action with the lowest Order, according to the following logic:
- If the inbound email action is active (the Active checkbox is selected), the system starts checking the incoming email according to the action conditions.
- If the action is not active, the system moves to the next one in Order.
- The email is checked against the conditions of the action.
- If the email does not match the conditions, the system skips the action and proceeds to check the next action from Step 1.
- Depending on the value of the Action type field, a Script is executed, or a Reply email is sent.
- The If the Active checkbox is disabled (its value is set tofalse), this inbound action is skipped. The inbound actions with the Active checkbox enabled (its value is set totrue)are processed further.
- If an email matches no condition of any inbound action, it passes all the way down the processing chain, and no action will be executed.
- If the condition of an inbound action is matched, the execution of the action script of that inbound action starts. The further processing flow depends on the value of the Stop processing when complete checkbox of this inbound action:is checked
- If the checkbox is
- selected, the
- rest of the
- actions down the chain are skipped, and the
- processing chain is terminated.
- If the checkbox is not selected, the
- system proceeds to the next action and repeats Steps 1–4.
- The email processing ends when the system completes all active actions or when an action is performed with the Stop processing when complete checkbox selected.
The email processing chain is shown in the diagram below:
 Image Added
Image Added
As a result, one inbound email can trigger execution of none, one or several action scripts in a row, depending on the values of the Active, Order and Stop processing when complete fields in each inbound action defined in the system.
 Image Removed
Image Removed
Configure an inbound email action
- Navigate to System Notification → Inbound Email Actions.
- Click New and fill in the fields.
- Click Save or Save and Exitexit to apply the changes.
| Tip |
|---|
Role required: admin. |
Inbound Email Action form fields
| Field | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | N | Specify an action name. |
| Action |
| type | N | Select the action type. Available options:
|
When the Reply Email option is selected, the action sends an email in reply when triggered.
|
|
|
| ||
| Message type | N | Specify a message type required to run the action. Available choice options:
|
|
|
| ||
| DSN | N | Select this checkbox to trigger the action in response to Delivery Status Notification emails |
. | ||
| Invitation | N | Select this checkbox to trigger the action in response to Invitation emails |
. | |
| Description | N |
| Add a detailed description of what this email action does. |
| Reply |
| N |
Enter the text of the reply letter. It |
will be sent to the |
original email address that |
initiated the |
action. | |
| From | Y |
Select a user, who initiates a script execution, or sends a response email. | ||
| Script | N | Enter a script that |
triggered by the inbound email action. You can use all methods of server-side API classes |
.
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Active | N | Select this checkbox to activate the action. | ||||||||
| Order | N | Enter a number to define the order of action processing. Actions are processed in ascending order |
| . | ||
Stop processing when complete | N | Select |
the checkbox to end the message processing after the current action is completed. All subsequent actions (with a higher Order) are ignored. |
Use case
You need to configure an inbound email action implementing the following logic:
When the system receives an email with the subject containing the keyword “access”“access”, a new incident is created and assigned to the group responsible for security and access to the system and data.
Create an inbound email action as shown below:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Create incident (access issue) |
| Action |
| type | Record Action |
| Message |
| type | New | |||||||||||||
| Active | true | |||||||||||||
| Script |
|
Inbound email action logging
Every inbound email action triggering is logged in the Script Logtable. You can filter these logs using the criteria below:
- Source IS Inbound Action
- Essence Document CONTAINS 0229fa8a-bcbe-1f11.
| Note |
|---|
The Essence Document field is responsible for email processed by the inbound email action. Enter the full address or a part of it, and use precision precise or imprecisionimprecise condition operators. |
. |
Recommendations
The incoming mail parsing returns the address value for the From field of a record from the Email (sys_email) table in lower case.
When searching for a user by the email by email in the Script column, do not use the IS operator because the value of email can be entered with uppercase letters. For example, J.Doe@mail.com.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
user.get('email', 'j.doe@mail.com'); |
Also, do not use the LIKE operator when searching for a user by email because the search will find a user with a similar email, for example, 'raj.doe@mail.com'.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
user.get('email', 'like', 'j.doe@mail.com') |
The following example shows the script with the userIDbyEmail() method that search searches for a user by email value:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
ss.importIncludeScript('EmailHelper');
class MyEmailHelper extends EmailHelper {
userIDbyEmail(email) {
const user = new SimpleRecord('user');
user.addQuery('email', 'startswith', email);
user.addQuery('email', 'endswith', email);
user.selectAttributes('sys_id');
user.setLimit(1);
user.query();
if (user.next()) {
return user.sys_id;
}
return this.searchGuest();
}
} |
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
/