Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
You can integrate your SimpleOne instance with any preferred active monitoring system (AMS) for supervising the stability and performance of your system. The AMS primary function is to query the service or CI status observation object statuses and generate alerts if necessary. After that, using the data exchange mechanism between the AMS and the SimpleOne instance, based on these alerts, events are created typified by the alert priority (these with the desired notification type and some parameters set by the monitoring rules. These may be exception events, warning events, and information events).
The event correlation engine allows configuring the system behavior rules depending on the event type (for example, whether or not to create an Incident if an Exception event has been thrown).following scheme shows the whole process of the monitoring and event management:
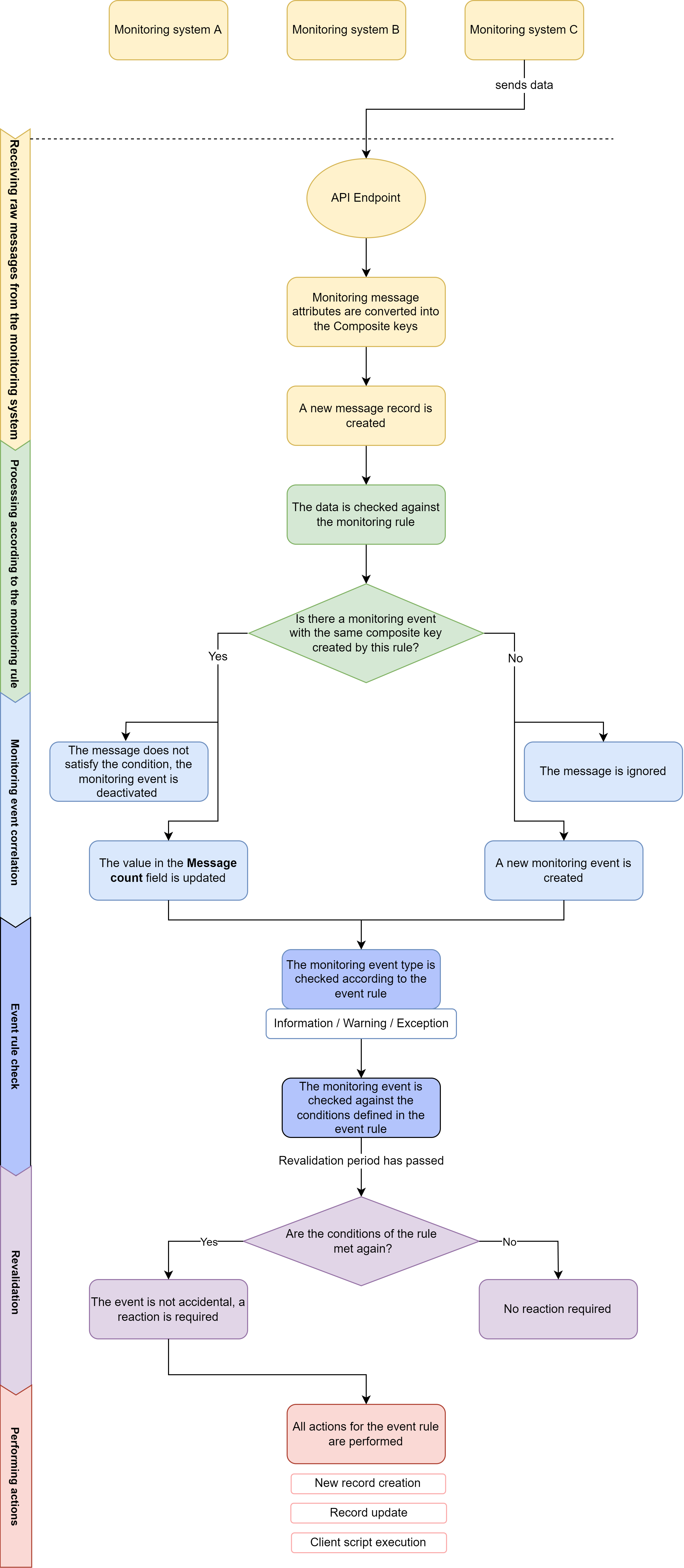 Image AddedThe rules listed below are provisional and can be configured in line with your business tasks and objectives.
Image AddedThe rules listed below are provisional and can be configured in line with your business tasks and objectives.
Exception Events
Exception Exception events are have the highest priority ones from on this list. An example of the an exception event can be unavailability of a server or any other crucial service unavailability.
The processing of exception events using the events correlation engine is listed below (we will use the example with the server):
- The AMS throws an alert sends a message: "
server is unreachable". - On the SimpleOne instance, in accordance with the settings monitoring rules specified, the Exception monitoring event was is created, based on identical to the alert message and having in the Active status.
- The Debounce Engine has started to work, and the specified period should pass before any actions can be undertaken (for example, three minutes).
- state.
- The event is checked against the event rule. The system starts counting down the revalidation period (for example, the period is three minutes). The period should pass before the revalidation. During this period, no actions can be undertaken.
- Once the period expires, the system checks the state Checking the status of the event associated with this alert the message (the monitoring system updates alert message states, and the event statuses states synchronize with them):
- If the event status state is still Active - – submit an infrastructure incident immediately.
- If the event status state has changed to Inactive, then the incident will not be created.
Warning Events
Warning events have less a lower priority than exceptions. An example of the a warning events event can be like "low disk space is running out, X Mb left".
The processing processing of warning events using the events correlation engine is listed below (we will use the example with the disk space):
- The AMS throws an alert looking alike : "
disk space is running out, X Mb left". - On the SimpleOne instance, in accordance with the settings monitoring rules specified, the Warning event was is created, based on identical to the alert and having in the Active status state.
- As opposed to the Exception events, we do not launch the Debounce engine and do not start a countdownthe system does not start counting down the revalidation period. In accordance with the settings specified, to launch the Debounce Engine revalidation period, there must be two active Warning events for this alert.
- If the second Warning event was is received, then the Debounce engine launches and the specified period revalidation periods starts. The period should pass before any actions can be undertaken.
- Checking the status After the period expires, the system checks the state of the events associated with this alert the message (the monitoring system updates alert statusesmessage states, and the event statuses states synchronize with them):
- If all the events are still Active - – raise an infrastructure incident immediately.
- If at least one event is Inactive, then an the incident will not be raised.
Information Events
Information events are the lowest-priority events, and they are merely informational. An example of the an information event is a user authorization notification. In there, it It is only necessary to gain obtain many similar events for a specified period, for example, ten login events attempts of the same user per minute.
The The processing of information events using the events correlation engine is listed below (we will use the example with the loginslogin attempts):
- The AMS sends a message about every unsuccessful attempt to log in to the system.: "
John Doe logs in". - The Monitoring and Event Management Event Monitoring module collects ten login events attempts of the same user per minute.
- After that, it the system raises an incident about incident about the suspicious activity. In this case, the Debounce Engine is not used.
This picture illustrates the basic principles of the work of the Event Correlation engine.
 Image Removed
Image Removed
ITSM Event table fields
Event type. Available options:
- Exception
- Warning
- Information.
The event state synchronized with the CI state in the AMS. Available choice options:
- Active
- Inactive.
Event Rule table fields
Event type. Available options:
- Exception
- Warning
- Information.
The period between throwing an event and raising an incident.
- the revalidation period is not used.
| Table of Contents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|