Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
An indicator is a rule of a time counter activation that is specified by proper conditions for starting, pausing, resetting and , and stopping this counter. It also determines a the time limit for declaring SLA as breached and contains and contains time conditions of a Commitment commitment type implementation.
For example, based on your SLA agreement,you can create separate SLA indicators for incidents that are having an impact from Low to Very High and set a separate Breach Time value for them, based on your SLA agreement.
When an indicator starts, the system automatically generates an Indicationindication, which is a time counter that tracks current timings and time points of the target service level commitment.
Depending on your business needs, you may need different types of indicatorindicators:
- standard – indicator creates indications that start at the moment or complete when specified conditions are met, or the duration ends.
For example, the start time is the moment when the task was assigned to John Doe. - retrospective – indicator creates indications which that count time basing based on the DateDate/Time field defined manually. Indications are created for records meeting specified conditions. To use this type of indicator, select the Defined by field option option in the Indication start time field and specify the field you need.
For example, the start time is the value of the Opened at field, and the indication is created for a record assigned to John Doe.
| Tip |
|---|
Role required: service_level_manager. |
Creating Indicator
To add a new Indicatorindicator, please complete the following steps:
- Navigate to Service Level Management → Indicator.
- Click New and fill in the form.
- Click Save or Save and Exit to apply changes.
The Indicator form
Field
Description
An indicator name.
| Note |
|---|
Please do not give the similar name to indicators when creating them against the same table; otherwise, they will work incorrectly if edited or deleted later. |
Specify a commitment type for this indicator. Available options:
- Resolution Time – the time it takes to resolve the issue (generally, this is the time from the issue is created to its state changed to Completed).
- Response Time – the time it takes to process the issue in a non-automated-way (generally, this is the from the issue is created to its state changed to In Progress).
Select this checkbox if you are creating an indicator on a parent table and it is necessary to use it against all of the child tables.
Example
The Service Requests table can be considered as a parent table, and every table extending it is a single service request.
Turning this attribute on, you can create a single indicator on a parent table which will affect every child table created.
Select one of two options:
- Defined by condition – for standard indications. Standard indication start time is the time when a record met the conditions defined in the Start Conditions tab.
- Defined by field – for retrospective indications. Retrospective indication start time is based on the value retrieved from the field specified in the Start time field. The record must also meet the conditions defined in the Start Conditions tab. Unlike the standard indication, the time when the conditions were met is ignored.
Define the column of the Date/Time type on the basis of which indications will be calculated, i.e. indications retrieve value for the start time from this column.
| Info |
|---|
The field appears if the Defined by field option is selected in the Indication start time field. |
- changes
- .
Business time measure the SLA runs before it is marked as Breached.
| Note |
|---|
Please note that all day duration (not only business hours) according to the chosen schedule is taken into account. See the calculation samples below this table. |
A working schedule selected from the list.
It determines working hours that the system uses when calculating an actual duration of the Commitment implementation under certain conditions.
To configure this timeline, use the Schedules features.
Determines an indicator Timezone.
| Note |
|---|
Only active timezones are available to choose.
Select one of the available records from the drop-down list if you need to specify a special timezone bond.
The default value is Indicator timezone. Available options:
- Caller's timezone
- CI location timezone
- Indicatos timezone
- Task location timezone
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Please keep in mind that if you create an inherited indicator on for a parent table, and after that a separate usual indicator on for a child table, the indications are to will be created only for a child table. |
Also, when creating an inherited indicator against for a parent table, please keep in mind remember that the extended attributes from child tables will not be available there. See the brief illustration below:
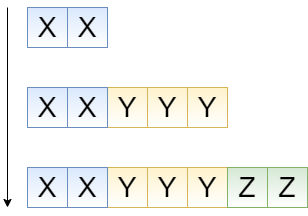
On this picture, the table set is displayed:
- The parent table, attribute set is XX
- The child table 1, attribute set is XXYYY
- The child table 2, attribute set is XXYYYZZ
Considering the fact that the Because attribute inheritance is going top-down, the table attributes (such as fields) that extend parent table tables will be inaccessible on the lower level. Please note that when configuring conditions of your indicator, make all critical attributes accessible on the top level.
Duration calculations
Example 1
Company A uses schedule "24x7", which means 24 working hours, 7 days a week, and around-the-clock shift-working, as an example. In this case, if work. If you enter "2" into the days field, this value is converted to 48 working hours or 2 working days. Nothing extraordinary.
Example 2
Company B uses schedule "8x5" schedule , which means 8 working hours, 5 days a week, one of the most common working schedules. In this case, if If you enter "2" into the days field, this value is converted to 48 hours (because there are 24 hours in a day), which gives 6 working days.
Specifying indicator conditions
To specify the conditions you need to fill in the following tabs:
Field | Required | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Conditions | Y | Establish conditions with the Condition Builder to make get the Indicator startstarted. The system uses the Table fields as transactional data to verify the conditions. When the transactional data changes, the system checks these conditions. E.g. , for incidents, it is appropriate to use Impact as a condition field with one of the possible values – Low, Medium, High, Very High. The When to cancel settingsetting allows to establish a condition forto start cancellation by one of the options below:
| ||
| Cancel Conditions | Y | This option appears when the Cancel conditions are met option is selected in the When to cancel field. It allows defining Define additional conditions to meet before the indicator cancels. In other words, if If the system meets these cancel conditions, it ignores the start conditions. | ||
| Pause Conditions | N | Establish conditions with the Condition Builder to make the Indicator indicator pause. The system uses the Table fields as transactional data to verify the conditions. When the transactional data changes, the system checks these conditions. E.g., for incidents, it is appropriate to useImpact as a condition field with one of the possible values – Low, Medium, High, Very High. The When to resume settingsetting allows to set a condition for pause resumption byusing one of the options below:
| ||
| Resume Conditions | Y | It The field allows defining additional conditions to meet be met before the indicator has previously paused resumes. In other words, if the system meets these resume conditions, it ignores the pause conditions.
| ||
| Complete Conditions | Y | Establish conditions with the Condition Builder to make the Indicator stop. The system uses the Table fields as transactional data to verify the conditions. When the transactional data changes, the system checks these conditions. | ||
| Reset Conditions | N | Establish conditions with the Condition Builder to make the Indicator reset. The system uses the Table fields as transactional data to verify the conditions. When the transactional data changes, the system checks these conditions.
|
| Note |
|---|
If an indication was is not on pause when the reset condition has conditions have been met:
If an indication was is on pause when the reset condition has conditions have been met:
|
| Table of Contents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|